Committed to safety.

Ensuring the safe and compliant transport of hazardous goods, our Dangerous Goods Solutions division based at our London Heathrow and Manchester facilities offer you the most reliable and secure methods of hazardous goods transportation. Our IATA and ADR qualified staff have the experience to provide tailored shipping solutions for all 9 of the dangerous goods classes, including full packing, re-packing and certification.
We offer a 24/7 – 365 day service at GBA DG Solutions. Our commitment to safety standards, fully qualified drivers and temperature-controlled conditions set us apart in the industry.
Our dedicated approach to staying up-to-date with regulations and our exceptional international supply chain are just a few of the measures we take to ensure the secure transportation of dangerous goods.
We offer our customers a one-stop shop for all shipments, from the first inquiry to arranging collection, packing or re-packing, certification and paperwork to ensure safe travel. At all times, our in-house customs clearance team will make certain that your goods are exported according to local government requirements. This ensures that both you and your customers remain compliant.
Our team will ensure movements are always fully monitored every step of the way to give you peace of mind.
- Consolidation Services
- Time critical NFO
- OOG
- Global Partner Network
- Regulated agent status
- In-house x-ray and ETD
- FCL
- LCL
- Reefer
- Global partner network
- UK & European network
- UK & European network – Aerospace
- European partner network
- European partner network – Aerospace
For any non-aerospace related Overland movements please follow the link to our GBA Logistics website where our colleagues in Freight Services will be happy to support your requirements.
- 24/7 customs support
- Tariff classification support
- Customs duty relief schemes
- Customs clearance instruction provision to 3rd party carriers
- Auditing services
- Badges at all UK airports and seaports
- Transit guarantee
- NCTS Approved
- ERTS facility
- Pre-checks to ensure documentation meets requirements for the selected mode of transport
- Saves time and money
- Packing or re-packing of dangerous goods using certified boxes in line with ADR, IATA and IMDG regulations
- Biopharma
- Oil and Gas
- Research and Development
- Institutes, Universities and Hospitals
- Aviation
- Life Sciences
- Chemical Companies
- RadioPharma
- Class 1: Explosives
- Class 2: Gases
- Class 3: Flammable liquids
- Class 4: Flammable and reactive solids
- Class 5: Oxidising agents & organic peroxides
- Class 6: Toxic and infectious substances
- Class 7: Radioactive material
- Class 8: Corrosives
- Class 9: Miscellaneous
- Real time track and trace
- Customer booking portal
- Experts in advising on AOG solutions: dedicated drives, FFO, charters, OBCs, air and crosstrade
- Key milestone notification
- Out of hours customs
Dangerous goods – Classes
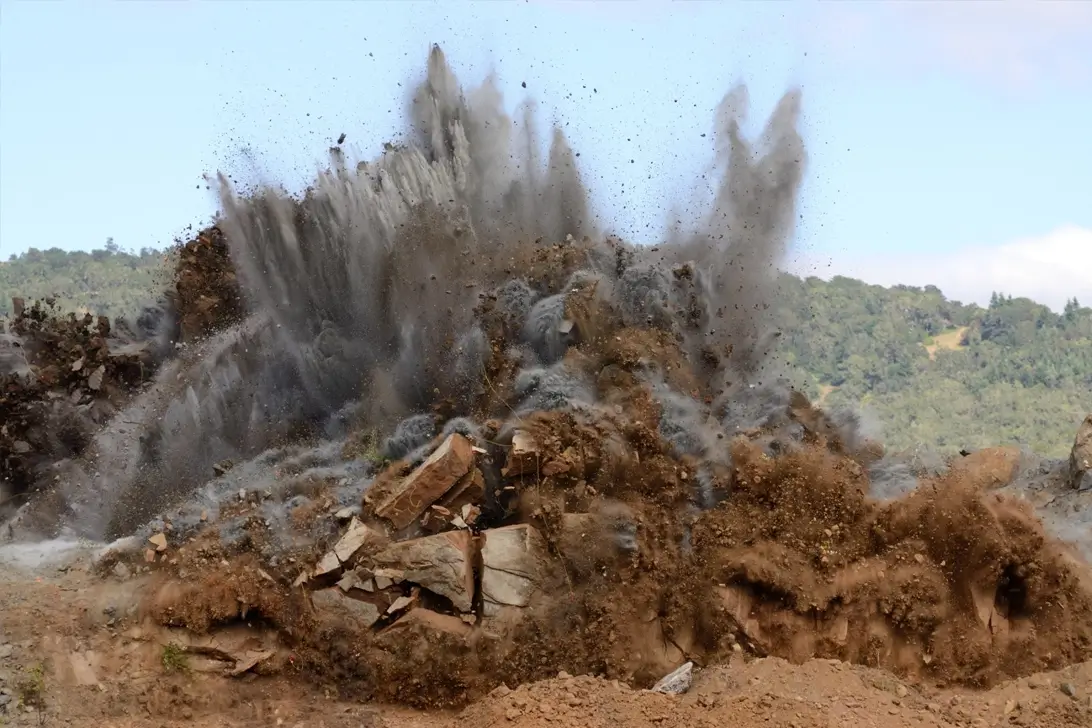

Class 1: Explosives
Explosives have molecules designed to rapidly change their (usually solid) state into very hot gas, in order to produce a sudden and violent physical effect.
There are 6 subdivisions:
- 1.1 Mass explosion hazard
- 1.2 Projection hazard only
- 1.3 Fire hazard and minor blast projection hazard
- 1.4 Minimal hazard
- 1.5 Blasting agents
- 1.6 Very insensitive detonating articles

Class 2: Gases
Class 2 consists of compressed gases, gases in their liquefied form, refrigerated gases, mixtures of gases with other vapours and products charged with gases or aerosols. These are considered hazardous goods for many reasons; often they are flammable, they can oxidize (chemically react with oxygen), act as asphyxiants and be toxic or corrosive.
- Division 2.1: Flammable gases
- Division 2.2: Non-flammable, non-toxic gases
- Division 2.3: Toxic gases
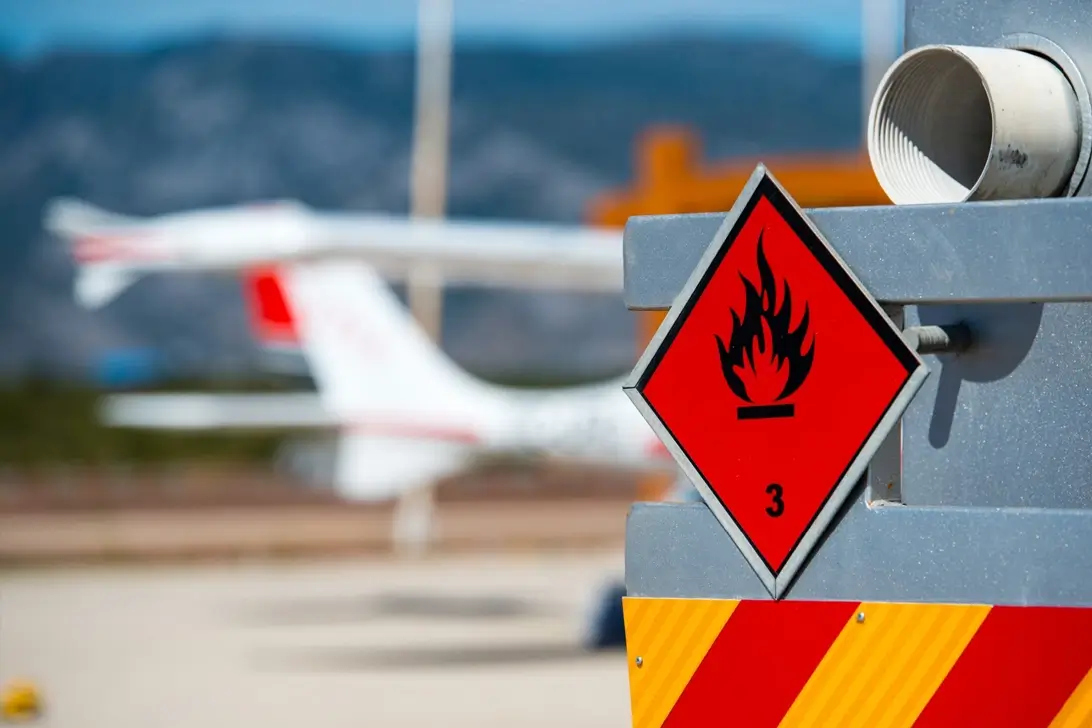



Class 3: Flammable liquids
Flammable liquids are liquids, mixtures of liquids or liquids containing solids that require a much lower temperature than others to ignite.
Often temperatures that may be reached during transportation.

Class 4: Flammable solids
Flammable solids; substances liable to spontaneous combustion; substances which emit flammable gases when in contact with water sub-divisions.
- Division 4.1: Flammable solids
- Division 4.2: Substances liable to spontaneous combustion
- Division 4.3: Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases
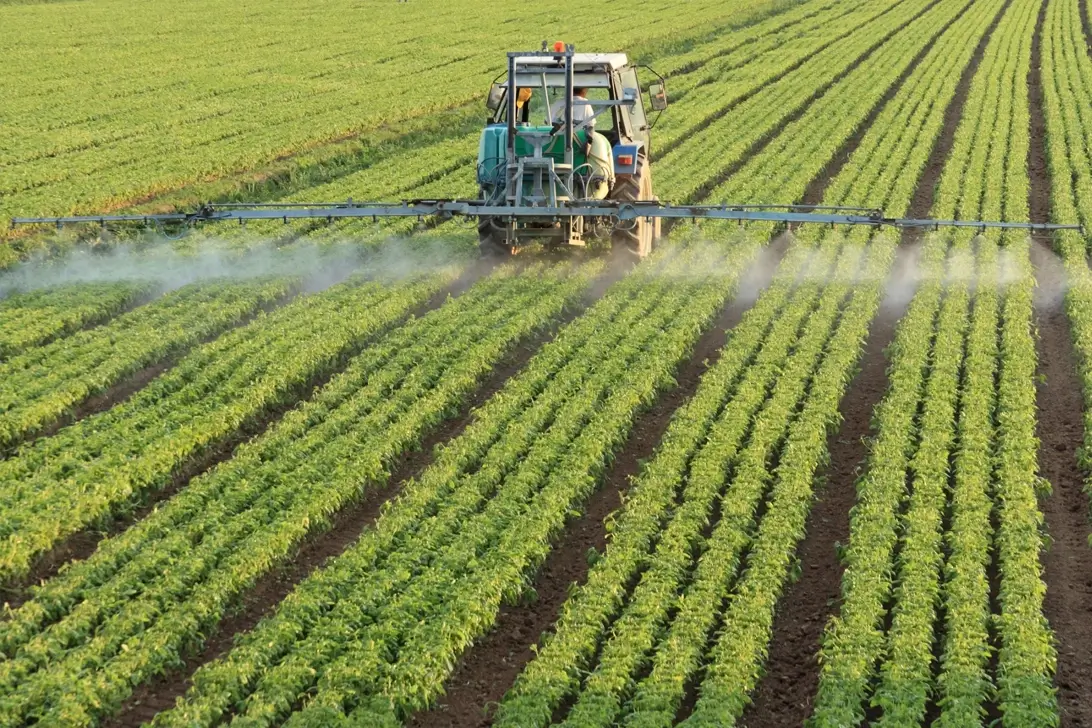



Class 5: Oxidising substances, organic peroxides
- Division 5.1: Oxidising substances
- Division 5.1: Organic peroxides
Class 5 goods – Also known as ‘oxidisers’ – are substances that can cause or be party to combustion typically by yielding oxygen as a product of chemical reactions.

Class 6: Toxic substances and infectious substances
- Division 6.1: Toxic substances
- Division 6.2: Infectious substances
Toxic substances are liable to cause death, serious injury or significant harm to human or animal health if they come into contact. This can be through swallowing, inhalation or skin contact.
Infectious substances are infectious and are likely to cause disease in humans or animals.
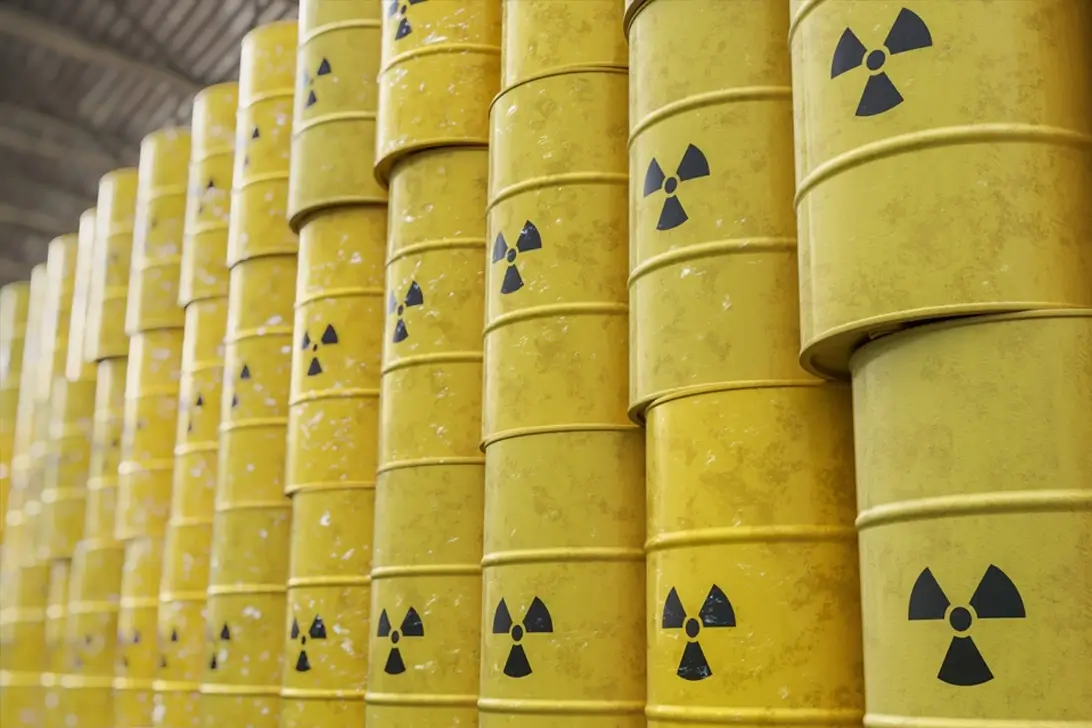


Class 7: Radioactive materials
Radioactive materials that emit ionizing radiation when they experience radioactive decay. This presents risks to human health.

Class 8: Corrosives
Corrosives are defined as dangerous goods because they are corrosive. Due to their nature, corrosive substances cause chemical reactions that degrade or disintegrate other materials when they come into contact with each other.
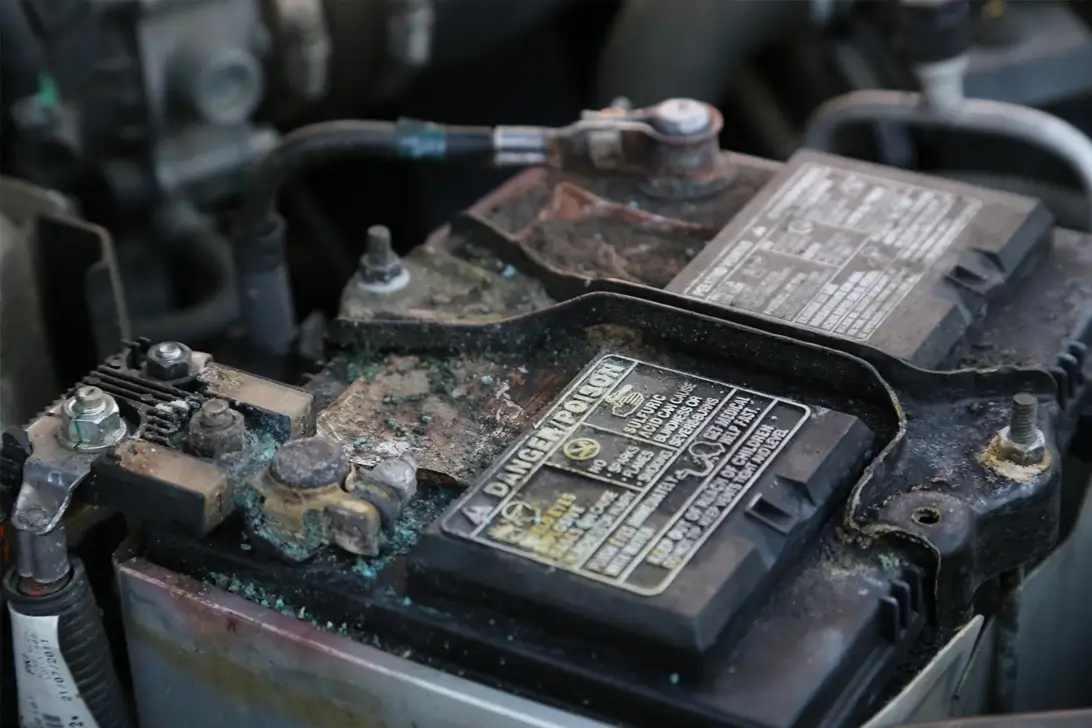



Class 9: Miscellaneous
Goods in Class 9 of dangerous goods are simply products that present dangers during transport that haven’t been covered in the other classes.
Dangerous goods – Classes


Class 1: Explosives
Explosives have molecules designed to rapidly change their (usually solid) state into very hot gas, in order to produce a sudden and violent physical effect.
There are 6 subdivisions:
- 1.1 Mass explosion hazard
- 1.2 Projection hazard only
- 1.3 Fire hazard and minor blast projection hazard
- 1.4 Minimal hazard
- 1.5 Blasting agents
- 1.6 Very insensitive detonating articles


Class 2: Gases
Class 2 consists of compressed gases, gases in their liquefied form, refrigerated gases, mixtures of gases with other vapours and products charged with gases or aerosols. These are considered hazardous goods for many reasons; often they are flammable, they can oxidize (chemically react with oxygen), act as asphyxiants and be toxic or corrosive.
- Division 2.1: Flammable gases
- Division 2.2: Non-flammable, non-toxic gases
- Division 2.3: Toxic gases


Class 3: Flammable liquids
Flammable liquids are liquids, mixtures of liquids or liquids containing solids that require a much lower temperature than others to ignite.
Often temperatures that may be reached during transportation.


Class 4: Flammable solids
Flammable solids; substances liable to spontaneous combustion; substances which emit flammable gases when in contact with water sub-divisions.
- Division 4.1: Flammable solids
- Division 4.2: Substances liable to spontaneous combustion
- Division 4.3: Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases


Class 5: Oxidising substances, organic peroxides
- Division 5.1: Oxidising substances
- Division 5.1: Organic peroxides
Class 5 goods – Also known as ‘oxidisers’ – are substances that can cause or be party to combustion typically by yielding oxygen as a product of chemical reactions.


Class 6: Toxic substances and infectious substances
- Division 6.1: Toxic substances
- Division 6.2: Infectious substances
Toxic substances are liable to cause death, serious injury or significant harm to human or animal health if they come into contact. This can be through swallowing, inhalation or skin contact.
Infectious substances are infectious and are likely to cause disease in humans or animals.


Class 7: Radioactive materials
Radioactive materials that emit ionizing radiation when they experience radioactive decay. This presents risks to human health.


Class 8: Corrosives
Corrosives are defined as dangerous goods because they are corrosive. Due to their nature, corrosive substances cause chemical reactions that degrade or disintegrate other materials when they come into contact with each other.


Class 9: Miscellaneous
Goods in Class 9 of dangerous goods are simply products that present dangers during transport that haven’t been covered in the other classes.

